Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment that involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room or chamber. This therapy has been explored for a wide range of medical conditions, with a significant focus on its potential to accelerate the healing process of injuries.
The concept behind HBOT is to enhance the body’s natural healing processes through the inhalation of 100% oxygen in a total body chamber, where atmospheric pressure is increased and controlled. This article delves into the mechanisms, applications, benefits, and limitations of using hyperbaric oxygen therapy for injuries, shedding light on its healing potential.
Introduction to Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is grounded in the basic principle of physics known as Henry’s Law, which states that the amount of a gas dissolved in a liquid is proportional to the pressure of that gas above the liquid, provided no chemical action occurs.
In the context of HBOT, this means that under increased atmospheric pressure, more oxygen can be dissolved into the bloodstream, tissues, and body fluids, potentially offering therapeutic benefits. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy Beverly Hills is an application of this principle, providing targeted treatments in a specific geographical location.
The Mechanisms Behind HBOT
At the heart of hyperbaric oxygen therapy’s healing potential is its ability to significantly increase the amount of oxygen dissolved in the plasma. This oxygen-rich plasma can travel to areas of the body where circulation is diminished or blocked, providing a boost in oxygen levels that can assist in the healing process.
The elevated oxygen levels in the body’s tissues stimulate various beneficial physiological effects, such as reducing inflammation, enhancing the effectiveness of the body’s natural immune responses, and promoting the growth of new blood vessels in areas of reduced circulation.
HBOT and Injury Healing
The healing process of injuries involves a complex sequence of physiological actions, including inflammation, new blood vessel formation, and tissue repair. By significantly elevating tissue oxygen levels, hyperbaric oxygen therapy can influence each of these phases. The increased oxygen availability can reduce swelling, mitigate pain, and provide the essential elements needed for the body to carry out repair processes more effectively.
Applications of HBOT in Injury Management
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been utilized in the treatment of various types of injuries, ranging from acute traumatic injuries to chronic wounds. Some specific applications include:
- Enhancing recovery from traumatic injuries ─ HBOT can accelerate the healing of fractures, crush injuries, and acute traumatic ischemias by improving oxygen delivery to damaged tissues.
- Treatment of chronic wounds ─ Conditions like diabetic foot ulcers can benefit from HBOT due to its ability to enhance wound healing, especially in hypoxic or infected wounds.
- Sports injuries ─ Athletes sometimes use HBOT to speed up the recovery from sports-related injuries, such as sprains, strains, and muscle fatigue, by reducing inflammation and promoting healing.
Scientific Evidence on HBOT’s Efficacy
The body of research on the effectiveness of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating injuries presents a mixed picture, with some studies showing significant benefits, while others suggest more research is needed.
Clinical trials have demonstrated HBOT’s positive outcomes in certain conditions, such as diabetic foot ulcers, by improving healing rates and reducing the need for amputation. However, the evidence varies greatly depending on the type of injury and the specific circumstances of the treatment.
Limitations and Risks of HBOT
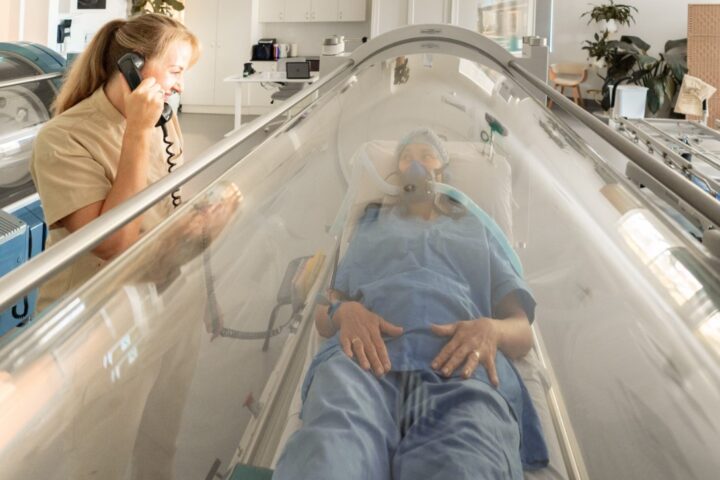
While hyperbaric oxygen therapy offers promising benefits for injury healing, it is not without its limitations and risks. The therapy requires specialized equipment and trained personnel, making it less accessible and more expensive than other treatments.
Moreover, HBOT is not suitable for everyone; certain medical conditions, such as untreated pneumothorax or certain types of ear and lung problems, may contraindicate its use. Potential side effects can include middle ear injuries, temporary vision changes, and, in rare cases, oxygen toxicity.
HBOT as Part of a Comprehensive Treatment Plan
It is important to recognize that hyperbaric oxygen therapy is not a standalone treatment but rather a complementary therapy that can enhance the overall treatment plan for injuries. Successful injury management often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including physical therapy, medication, surgery, and lifestyle modifications, with HBOT potentially playing a supportive role.
Future Directions in HBOT Research
The future of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in injury treatment looks promising, with ongoing research exploring its full potential and limitations. Advances in technology and a deeper understanding of the biological effects of high oxygen levels may lead to more precise applications of HBOT, tailored to individual patient needs and specific types of injuries.
Personalized Treatment Protocols with HBOT
The individual variability in response to hyperbaric oxygen therapy necessitates the development of personalized treatment protocols. Factors such as the type and severity of the injury, the patient’s overall health status, and the presence of underlying conditions can significantly influence the effectiveness of HBOT.
Tailoring the number of sessions, the duration of each session, and the specific pressure levels to the individual’s needs could optimize the therapy’s benefits and minimize potential risks.
Ethical Considerations in HBOT Use
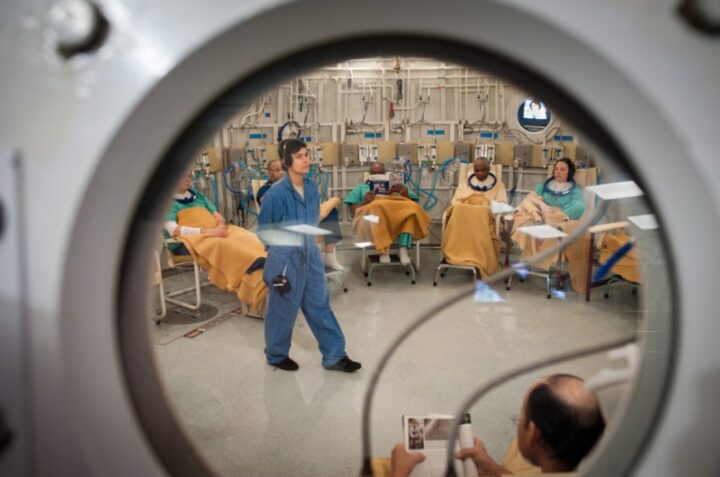
As with any medical intervention, ethical considerations play a crucial role in the application of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. The decision to use HBOT should be based on a careful evaluation of its potential benefits and risks in each case.
Informed consent is paramount, ensuring that patients are fully aware of the therapy’s experimental nature for certain conditions and understand the possible outcomes and side effects. The cost of HBOT, given its requirement for specialized equipment and facilities, also raises ethical questions regarding its accessibility and equity in healthcare.
Conclusion
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy holds intriguing potential for aiding in the healing of various injuries, leveraging the power of oxygen to enhance the body’s natural repair processes. While the evidence supporting its efficacy is growing, it is crucial to approach HBOT with a balanced perspective, considering its benefits in the context of its limitations and risks.
As research continues to evolve, the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in injury management may become clearer, offering new avenues for improving patient outcomes.




